TMG Home Page
2D automatic triangular mesh generator
The TMG code is based on the advancing front technique, and provides
a way to triangulate general domains in two dimension, possibly
divided into subdomains, with holes, and with curved boundaries.
The code is written in C, and the graphical part requires an interface
with xview, denoted xsti.
This works fine under Linux, but requires version 3.2p1.4-4 (or later) of the xview
package (can be found e.g. on the contrib part of RedHat 5.1),
and not so fine under Solaris.
Download via ftp from
ftp.dmf.unicatt.it or
via http from
dmf.unicatt.it.
The development version is maintained in the subversion repository https://svn.dmf.unicatt.it/svn/projects/software/tmg
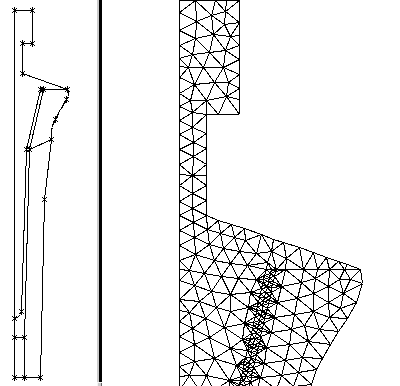 An example of typical domain divided into subdomains and
a zoom of the resulting
mesh after flipdiag and pigra
regularization.
The file
An example of typical domain divided into subdomains and
a zoom of the resulting
mesh after flipdiag and pigra
regularization.
The file
protesi.tmg
contains the domain description.
The mesh in the picture is obtained from the domain description
file with the TMG command sequence:
TMG> mesh
TMG> flipdiag
TMG> pigra
TMG> flipdiag
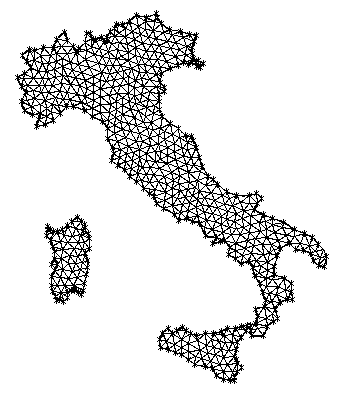 Here is another example...
Here is another example...
 And an example with a hole.
It is also possible to mesh the interior of the hole
as well by using multiple subdomains.
Here is a gif image of the resulting mesh.
And an example with a hole.
It is also possible to mesh the interior of the hole
as well by using multiple subdomains.
Here is a gif image of the resulting mesh.
Related information
MP.
Last modified January 19, 2016.
 Validate!
Validate!
 An example of typical domain divided into subdomains and
a zoom of the resulting
mesh after flipdiag and pigra
regularization.
The file
An example of typical domain divided into subdomains and
a zoom of the resulting
mesh after flipdiag and pigra
regularization.
The file
 Here is another example...
Here is another example...
 And an
And an